Basic operation flow of warehouse (1): goods entering and leaving the warehouse
Double Eleven is coming, and the whole people enjoy shopping spree. It is better to say online shopping spree than shopping spree. Online shopping has almost subverted our lifestyle. While enjoying the convenience brought by online shopping, have you ever thought about what is behind the convenience? Who brings us convenience? This article takes you to find out!

In actual business, the receipt, delivery, purchase and management of goods are all handled by the warehouse, and the owner only needs to send the task order to the warehouse.
The following is a brief introduction to the basic operation process of goods warehousing and outbound:
The warehousing process of goods is as follows:

When the owner needs to store the purchased goods in the warehouse, he needs to create the warehousing task first. The tasks created include the details and quantity of goods to be put into storage, as well as the estimated storage time. After the task is successfully created, it is submitted to the warehouse, waiting for the warehouse to arrange warehousing.
After receiving the warehousing task, the warehouse operates according to the following process:

- The warehouse formulates the warehousing task plan and informs the corresponding drivers of the transportation task;
- The driver loads the car at the designated place and transports the goods to the warehouse within the specified time;
- After arriving at the warehouse, the driver should give the delivery note to the warehouse receiver, who will check the delivery note with the receipt to confirm that the receiving task is correct, and then check whether the vehicle meets the requirements, whether the outer packaging of the goods is damaged, and whether the model is consistent with the packing list to prevent unqualified goods from entering the warehouse;
- After it is confirmed, it starts unloading and receiving goods, and PDA scans the arrival notice number and enters the receiving task; PDA usually has two receiving methods, ordinary receiving and container receiving. Ordinary receiving directly scans the barcode of goods and inputs the quantity of goods to complete receiving. Container receiving needs to scan the container code and commodity bar code, associate the container with the commodity, and concentrate the commodity into the container to complete receiving.
Before unloading, only the outer packaging of the goods is inspected, and after unloading and receiving, it is necessary to disassemble the outer packaging to inspect the goods more carefully.
The receiver counts the quantity of the goods according to the arrival notice, and clearly marks the actual number of pieces collected, and at the same time verifies the quality problems of the goods (damaged, damp and short-packed). The goods that pass the acceptance are packed in the specified position and waiting for the shelves.
After the inspection, the receiver will feedback the warehousing notice to the owner and the driver to inform that it has been warehousing.
The last step of warehousing is putting on shelves.
The warehouse staff assigns locations to the goods to be put into storage in advance, and then the shelf staff puts the goods on the designated locations. Corresponding to the two receiving methods mentioned above, there are two ways to put goods on shelves, namely, ordinary shelves and container shelves.
The difference between ordinary shelves and container shelves is simply that goods are put on single shelves and put on shelves in batches.
The basic process of ordinary shelves:

Basic process of container shelving:

Judging from the process of putting containers on shelves, some students may have doubts. When putting containers on shelves, they only established the corresponding relationship between containers and locations, but not between commodities and locations. How can we find locations through commodity barcodes in the future? Or how to query the goods of the location through the barcode of the location?
In fact, commodities, containers and warehouses are interrelated:
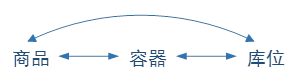
The establishment of the corresponding relationship between containers and locations indirectly establishes the relationship between commodities and locations, and the corresponding relationship between commodities and containers has been established at the time of receiving goods, so the commodities on the container shelves can be directly queried through locations.
After the shelves are completed, the warehousing process of goods is basically completed.
The process of goods delivery is complicated, usually including picking, broadcasting, checking, packaging, sorting, collecting and handing over, etc. This process is not only manual labor for warehouse staff, but also careful in any step, otherwise it will cause losses to warehouse, seller and buyer. Especially in the peak period of double eleven commodity circulation, warehouse staff should be vigilant to avoid mistakes.
The basic process of goods delivery is as follows:
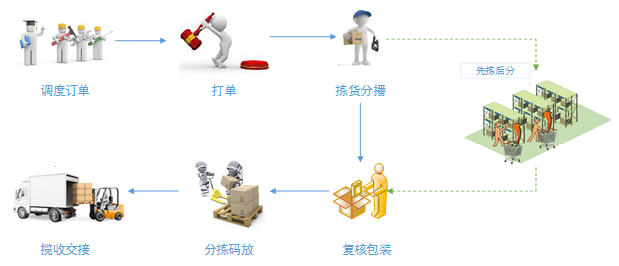
Online shopping orders will first flow into the seller’s OMS system (order management system), and the owner will push the orders to the WMS system of the warehouse after confirmation by OMS.
WMS system usually needs to schedule orders first, which is simply to classify orders according to certain rules. There are many factors that affect order classification in actual business, so scheduling seems simple, but the logic behind it is very complicated. The main functions and purposes of scheduling orders are as follows:
(1) Matching the optimal warehouse for the order:
For example, a shipper usually has multiple warehouses, so choosing the warehouse closest to the consignee is undoubtedly the fastest and most cost-saving.
In actual scheduling, the selection of warehouses depends not only on distance information, but also on inventory information, goods information, carrier information and so on.
In order to achieve the best transportation scheme, it is often necessary to split the order.
For example, an order contains two kinds of goods, A warehouse is the closest to the consignee, but the inventory information of A warehouse shows that there is only A goods, but there is no B goods, and B warehouse, which is far away from the consignee, has sufficient inventory. At this time, it is necessary to split the order into two orders, one of which is only A goods allocated to A warehouse, and the other is only B goods allocated to B warehouse, and the two warehouses are delivered to the consignee respectively.
Although such bill splitting operation has achieved cost reduction and efficiency increase, it often leads to the bad experience of the consignee receiving goods many times, so the bill splitting operation should be cautious.
(2) Match the best carrier for the order.
When the owner has a designated carrier, assign the carrier to the order; When the owner does not specify a carrier, the distance information from the warehouse to the consignee, freight information, inventory information and goods information are comprehensively considered, and the most suitable carrier is matched for the order according to certain rules.
(3) make production plan for the warehouse
The warehouse system receives a lot of orders every day, especially on special days such as "6.18", "11.11" and "12.12", and the order quantity is beyond imagination.
Therefore, it is necessary to plan the daily production plan of the warehouse in advance, so that the warehouse can handle all orders in an orderly manner and try to avoid unexpected situations during the peak order period.
In addition: in a large number of orders, there are often many orders with the same or similar goods, so it will save a lot of time to concentrate on the production and picking of these orders.
(4) Planning the picking route for the picker.
There are thousands of goods stored in the warehouse. Although it is mentioned earlier that each commodity has a corresponding location, goods can be searched according to the location, but the warehouse is large and the locations are widely distributed, and the goods in the picking task are not concentrated in a certain location. If the picking route planning is unreasonable, pickers need to go back and forth to different reservoir areas to find them, resulting in low efficiency and other problems.
Scheduling can query the inventory position of goods according to the order information, and then plan the shortest picking route according to the inventory position, which greatly improves the picking efficiency.
Above all, scheduling is a process of pre-processing and classifying orders, in which many optimization strategies will be generated to guide the subsequent operations of the warehouse, and warehouse personnel can perform various operations according to the scheduling results.
After the scheduling, the order flows to the corresponding warehouse system, and the order is selected in the WMS system to generate the picking task and print the task list. The basic information of the order is on the face sheet, and the outer packaging of the goods needs to be affixed with the face sheet to facilitate the delivery staff and the consignee to distribute and identify the package according to the face sheet information.
Some warehouses print face sheets on the packaging platform, which has the advantages of being easy to use and avoiding the loss and confusion of face sheets in the picking process.
After the picking task is generated, it is assigned to the picker, who downloads the picking task on PDA, picks up the correct quantity of goods from the designated warehouse according to PDA’s instructions and puts them into the picking truck. There are two kinds of picking operations: picking before sorting and picking while sorting.
Picking before sorting is to separate picking and sorting. First, collect all the goods in the task order into the pickup truck, and then distribute the goods on the sowing wall. The seeding wall is a cart with many cells, each cell corresponds to an order, and seeding is to classify the goods in the pickup truck into each cell according to the order.
Picking and dividing is to put the goods into the corresponding cells when picking. Before picking, the picker binds the cell to the order one-to-one. When pushing the sowing wall to pick the goods, the PDA scans the barcode of the goods and automatically prompts which cell the goods should be put in, thus realizing the sorting while picking.
Although picking while sorting can be completed in one step, picking before sorting is more used in practical scenes, because the seeding wall is larger than picking trucks, and it is inconvenient to move in the reservoir area, which is not conducive to the work of pickers.
After the goods are placed in the sowing wall, they will go to the packaging station for review and packaging.
The packager rechecks the face sheet code and commodity code by computer scanning. On the one hand, he checks the quantity and type of commodities to prevent the wrong delivery and missing delivery of commodities; on the other hand, he checks the quality of commodities to prevent defective products from leaving the warehouse.
After the re-inspection, the packager packages the goods and puts the corresponding face sheet on the outer packaging, and then puts the package on the conveyor belt to enter the next link.
On the conveyor belt, the sorting robot automatically sorts the packages according to different express delivery by scanning the information of the packages. At the end of the conveyor belt, the sorting personnel put the package codes of different express delivery in the designated area to wait for collection.

After all the goods in the delivery task are sorted, the warehouse informs the courier to collect them at the specified time and print the handover list at the same time. After the courier arrives at the warehouse, he checks the goods according to the handover list provided by the warehouse, and uses PDA to scan the goods list to receive the goods. After receiving the goods is confirmed to be correct, the courier signs the handover list to complete the handover, and finally loads the goods and leaves the warehouse.
The above is the basic operation flow of goods in and out of the warehouse. Due to the different needs of different businesses, there will be differences in the operation flow.
In addition to warehousing and warehousing, the basic operation processes of the warehouse include inventory, tally and replenishment, which will be introduced later.
This article was originally published by @ Xiaobaitoo. Everyone is a product manager. It is forbidden to reprint without permission.
The title map comes from Unsplash and is based on CC0 protocol.